- Spine Clinic
- About Our Spine Clinic
- C-Spine
- L-Spine
- Joint Clinic
- About Our Joint Clinic
- Knee
- Shoulder
- Hips
- Small Joint Clinic
- About Our Small Joint Clinic
- Hand
- Foot

+82-31-783-9623
+82-10-2783-6676
Our medical experts at BSH promise to provide honest and exceptional care.
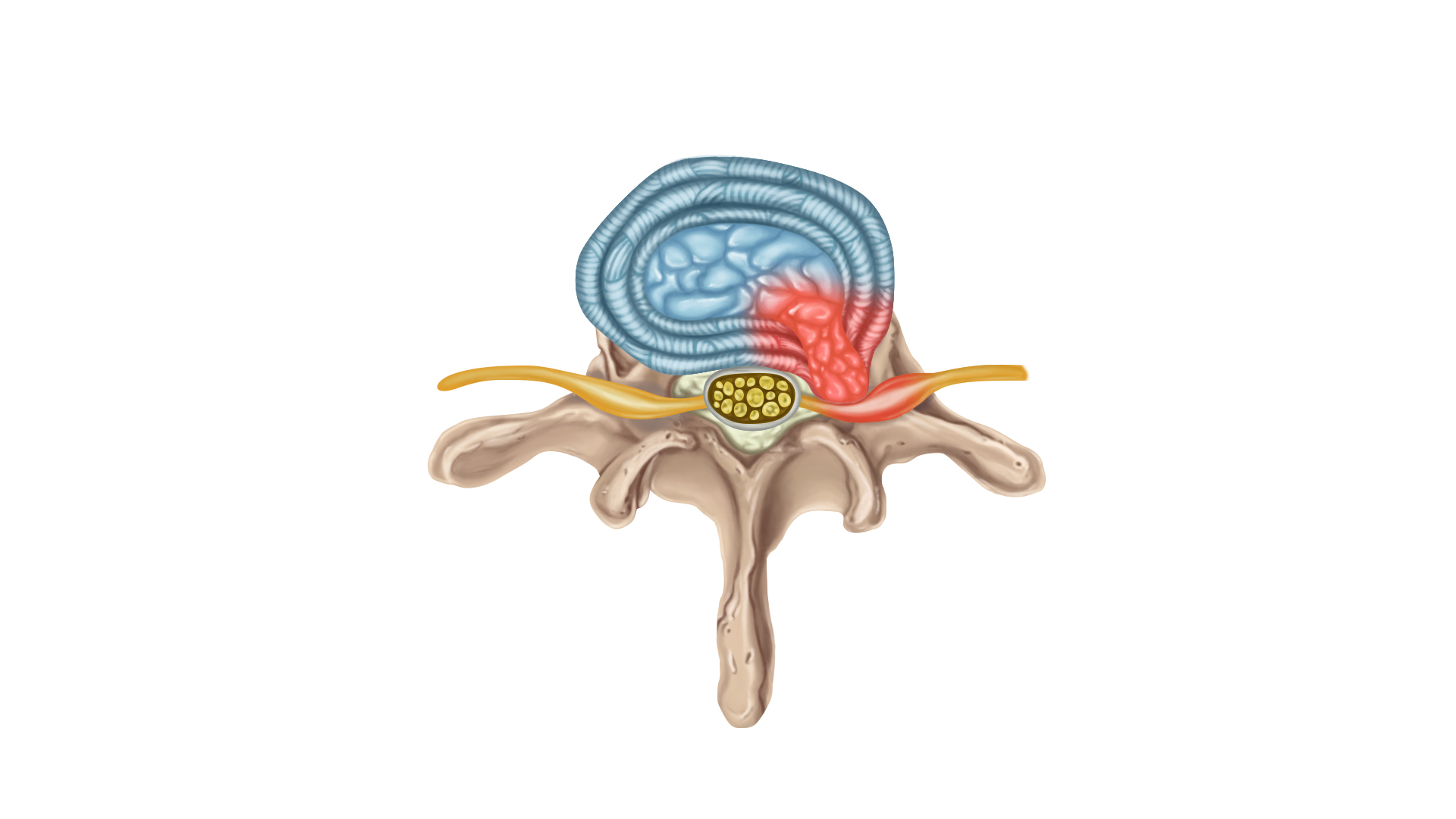
 Repetitive activities that strain your spine
Repetitive activities that strain your spine Improper lifting
Improper lifting Staying seated for a long time (such as frequent driving)
Staying seated for a long time (such as frequent driving) Poor posture
Poor posture Being overweight or excessive drinking and smoking
Being overweight or excessive drinking and smoking Frequently wearing high heeled shoes
Frequently wearing high heeled shoes Pain in the lower back, pelvis, and legs
Pain in the lower back, pelvis, and legs Numbness or tingling sensation in the hip, leg, and/or foot
Numbness or tingling sensation in the hip, leg, and/or foot Stiffness in the back
Stiffness in the back Pain in coughing, sneezing, or during bowel movement
Pain in coughing, sneezing, or during bowel movement Pain when seated
Pain when seated Straight leg raise test: In this test, you lie on your back and your doctor lifts your affected leg while your knee stays straight. If you feel pain down your leg and below the knee, you are strongly suspected to have lumbar disc herniation.
Straight leg raise test: In this test, you lie on your back and your doctor lifts your affected leg while your knee stays straight. If you feel pain down your leg and below the knee, you are strongly suspected to have lumbar disc herniation. The doctor will also do a nerve examination where you lie on your stomach and lift your leg up so that your heel will touch your hip. If there is pain or any other abnormal changes, you may have lumbar disc herniation
The doctor will also do a nerve examination where you lie on your stomach and lift your leg up so that your heel will touch your hip. If there is pain or any other abnormal changes, you may have lumbar disc herniation To help confirm the diagnosis, an MRI is needed to see a clear and detailed image of your back.
To help confirm the diagnosis, an MRI is needed to see a clear and detailed image of your back. Conservative Treatment
Conservative Treatment
If your condition is in the initial stages or not severe, rest, medication (anti-inflammatory and muscle relaxant), physical therapy, and massage therapy may be recommended.
 Non-surgical Treatment
Non-surgical Treatment
If conservative methods provide no relief, a non-surgical treatment option such as Epidural Decompression is available. Epidural injections (thickness of 1mm) are administered into the epidural space to reduce inflammation of the nerve and the disc.
 Surgical Treatment
Surgical Treatment
If your condition is severe, you may need surgery. Minimally Invasive Arthroscopic laminectomy is a surgery where a tiny incision is made and the ruptured disc is removed. This requires an overnight hospital stay of 2~3 days.